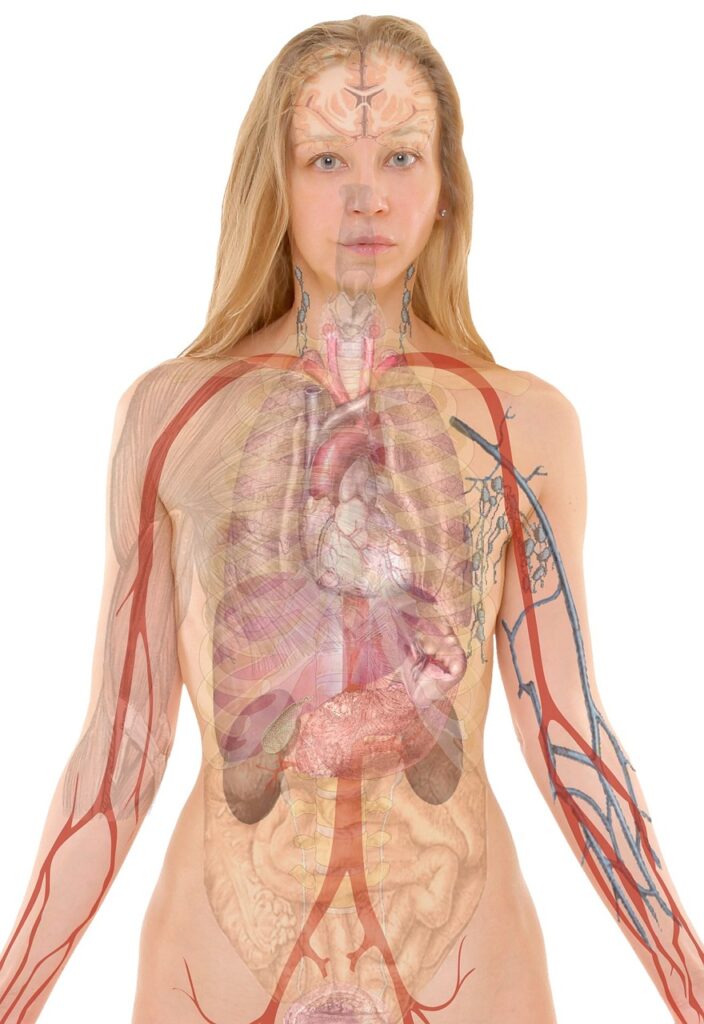
What is Stress and What Does It Cause in Our Bodies?
Stress is the body’s natural response to challenging, threatening, or overwhelming situations. It is a reaction that activates both the nervous and hormonal systems to help us face a specific situation (acute stress) or manage ongoing pressures (chronic stress).
Types of stress
- Acute Stress: An immediate response to a challenge or danger, such as an exam or an emergency.
- Chronic Stress: Occurs when tensions are constant, such as work, financial, or health problems.

Effects of Stress on the Body:
1. Nervous System:
- Release of Stress Hormones: Hormones like cortisol and adrenaline are released, increasing heart rate, breathing, and blood pressure.
- Overactivation: This can lead to mental and emotional fatigue.
2. Cardiovascular System:
- Increased Blood Pressure: This raises the risk of heart disease and strokes.
- Rapid Heartbeat: It can lead to palpitations or arrhythmias.
3. Immune System:
- Weakening: Prolonged stress reduces the body’s ability to fight infections and diseases.
- Chronic Inflammation: Contributes to issues such as arthritis or autoimmune disorders.
4. Digestive System:
- Gastric Problems: Includes heartburn, nausea, or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
- Appetite Changes: Can lead to overeating or weight loss.
5. Endocrine System:
- Hormonal Imbalances: Can affect the menstrual cycle, fertility, and metabolism.
6. Mind and Emotions:
- Anxiety and Depression: Resulting from the inability to cope with constant pressure.
- Sleep Problems: Such as insomnia or nightmares.
- Irritability and Difficulty Concentrating: Stress can lead to heightened irritability and challenges in focusing.
7. Muscles and Joints:
- Muscle Tension: It causes headaches, neck, back, and jaw pain.
5 Simple Ways to Manage Stress
- Physical Exercise: Releases endorphins that help reduce stress.
- Relaxation: Practices like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing techniques promote relaxation.
- Good Nutrition: A balanced diet helps the body cope with stress more effectively.
- Adequate Rest: Sleep is crucial for both mental and physical recovery.
- Social Support: Talking with friends, family, or therapists can help alleviate stress and tensions.
Tips for Managing Stress:
1. Relaxation Techniques:
- Deep Breathing: Practice slow abdominal breathing by inhaling through your nose for 4 seconds, holding the air for 4 seconds, and then exhaling slowly for 6-8 seconds. This technique helps activate the body’s relaxation response and reduces stress.
- Meditation: Dedicate 5-10 minutes each day to meditate using apps like Headspace or Calm, or simply sit in silence and focus on your breath. Meditation calms the mind, reduces anxiety, and enhances mental clarity.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: Tense and then relax specific muscle groups, starting from your feet and working your way up to your head. This technique helps release physical tension, promotes relaxation, and improves body awareness.

2. Organization and Time Management:
- Prioritize Your Tasks: Use a to-do list and highlight the most important tasks. The Eisenhower Matrix is a helpful tool for categorizing tasks based on urgency and importance, ensuring you focus on what truly matters.
- Set Boundaries: Learn to say “no” to unnecessary commitments. This helps prevent overloading yourself, reducing stress and allowing time for what is most important.
- Regular Breaks: Work in time blocks, such as the Pomodoro Technique (25 minutes of work followed by a 5-minute break), to maintain focus and productivity while preventing burnout. Regular pauses help refresh your mind and sustain energy throughout the day.

3. Physical Activity:
- Regular Exercise: Activities such as yoga, swimming, cycling, or walking for 20-30 minutes can reduce cortisol levels and release endorphins, which help improve mood and reduce stress.
- Mindful Movements: Practice gentle stretching or tai chi to relax both the body and mind. These mindful movements promote relaxation, enhance flexibility, and help clear mental tension.
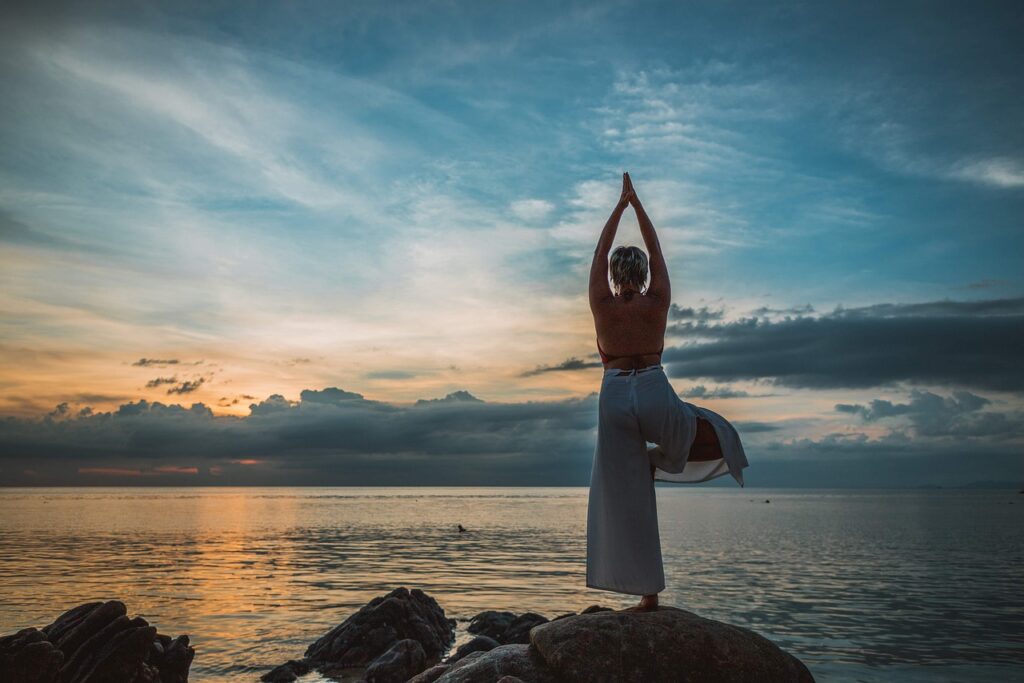

4. Healthy Lifestyle:
- Proper Nutrition: Include foods rich in magnesium (nuts, spinach), omega-3 (salmon, chia), and vitamin B (whole grains). These nutrients support brain function, reduce inflammation, and help regulate mood, contributing to stress management.
- Avoid Stimulants: Limit caffeine and alcohol intake, as they can exacerbate stress and disrupt sleep. These substances can increase anxiety levels and negatively impact your physical and mental health.
- Restorative Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep. Create a relaxing nighttime routine, and avoid screens before bed to improve the quality of your sleep. Proper rest is crucial for physical and emotional recovery, helping to reduce stress and maintain overall well-being.
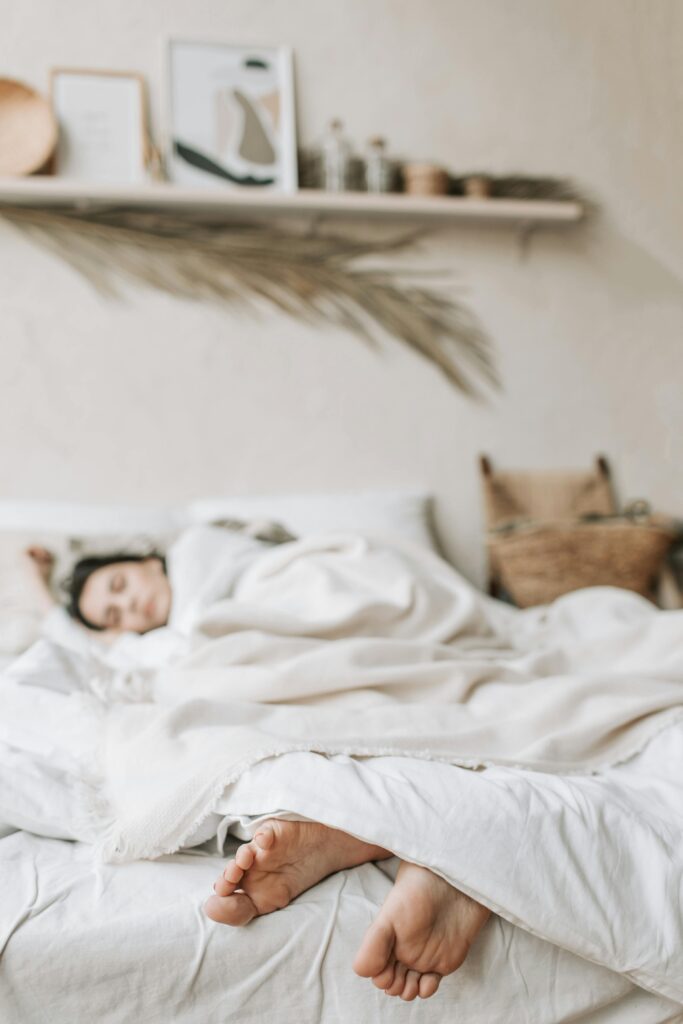

5. Social and Emotional Support:
- Talk to Someone: Share your concerns with friends, family, or a therapist. Expressing your feelings can help reduce stress, provide clarity, and offer support from others who care about you.
- Dedicate Time to Social Activities: Spending time with trusted people strengthens your emotional support network. Social connections help alleviate feelings of isolation and provide opportunities for relaxation and fun, which can reduce stress.
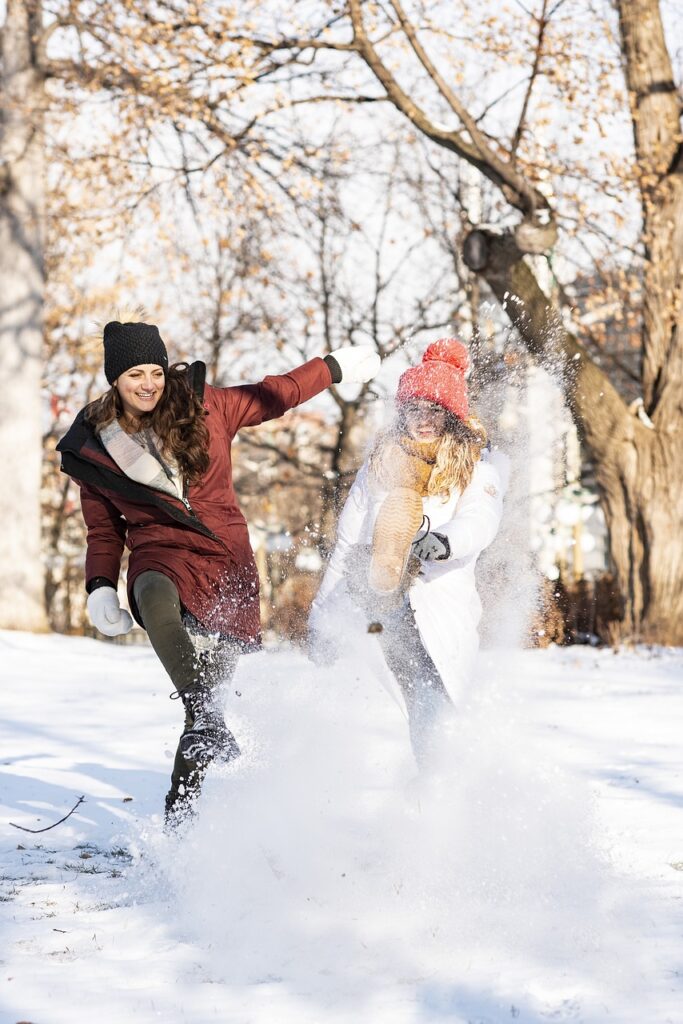

6. Mental and Attitude Changes:
- Practice Gratitude: Write down 3 things you’re grateful for each day. This helps shift your focus to the positive aspects of your life, promoting a mindset of abundance and contentment.
- Accept What You Can’t Change: Focus on what is within your control and learn to let go of what isn’t. Accepting the uncontrollable can reduce anxiety and increase emotional resilience.
- Create Positive Thoughts: Replace “I can’t handle this” with “I will take it step by step.” Shifting your inner dialogue to a more constructive mindset helps build confidence and reduces stress.
Be grateful for what you already have while pursuing your goals. If you’re not grateful for what you have, what makes you think you’ll be happy with more?
Roy T. Bennett
Alternative Therapy
- Aromatherapy: Use essential oils such as lavender or eucalyptus to induce calm and relaxation. These oils are known for their soothing properties that help reduce stress and promote mental clarity.
- Therapeutic Writing: Keep a journal to express emotions and organize thoughts. Writing can be a powerful tool for managing stress, helping you process feelings, reflect on experiences, and gain perspective.

If you feel that stress persists or interferes with your daily life, consult a mental health professional for additional support.
Disclaimer:
The information provided about stress management is for informational and educational purposes only. It is not intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you are experiencing stress levels that significantly impact your quality of life, physical or mental health, we recommend seeking help from a certified healthcare professional. The suggested methods may not be suitable for everyone, so it is important to tailor strategies to your needs and circumstances.
This blog may contain sponsored content or affiliate links. This means that, in some cases, I may receive monetary compensation or in-kind benefits for recommendations, mentions of products, services, or companies, at no additional cost to you.
I assure that all opinions expressed are sincere and reflect my personal experience, regardless of any sponsorship received. I always prioritize sharing useful and relevant information for my readers.
If you have questions about the nature of any sponsored content, feel free to contact me for more information.
The key is not to prioritize what’s on your agenda, but to schedule your priorities.
Stephen Covey